Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that involves teaching machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. The machine learning algorithms automatically learn patterns and insights from the data and use that learning to make predictions or decisions on new and unseen data. It is a data-driven approach that enables computers to improve their performance on a specific task as they gain more experience, without human intervention.
Machine Learning is needed because it enables computers to learn and improve from experience and data, which can lead to more accurate and efficient predictions, decision-making, and automation of tasks. For example, machine learning is used in image recognition, speech recognition, natural language processing, fraud detection, recommendation systems, and many other applications that rely on pattern recognition and prediction.
How is it different from AI, Deep Learning, and Data Science?
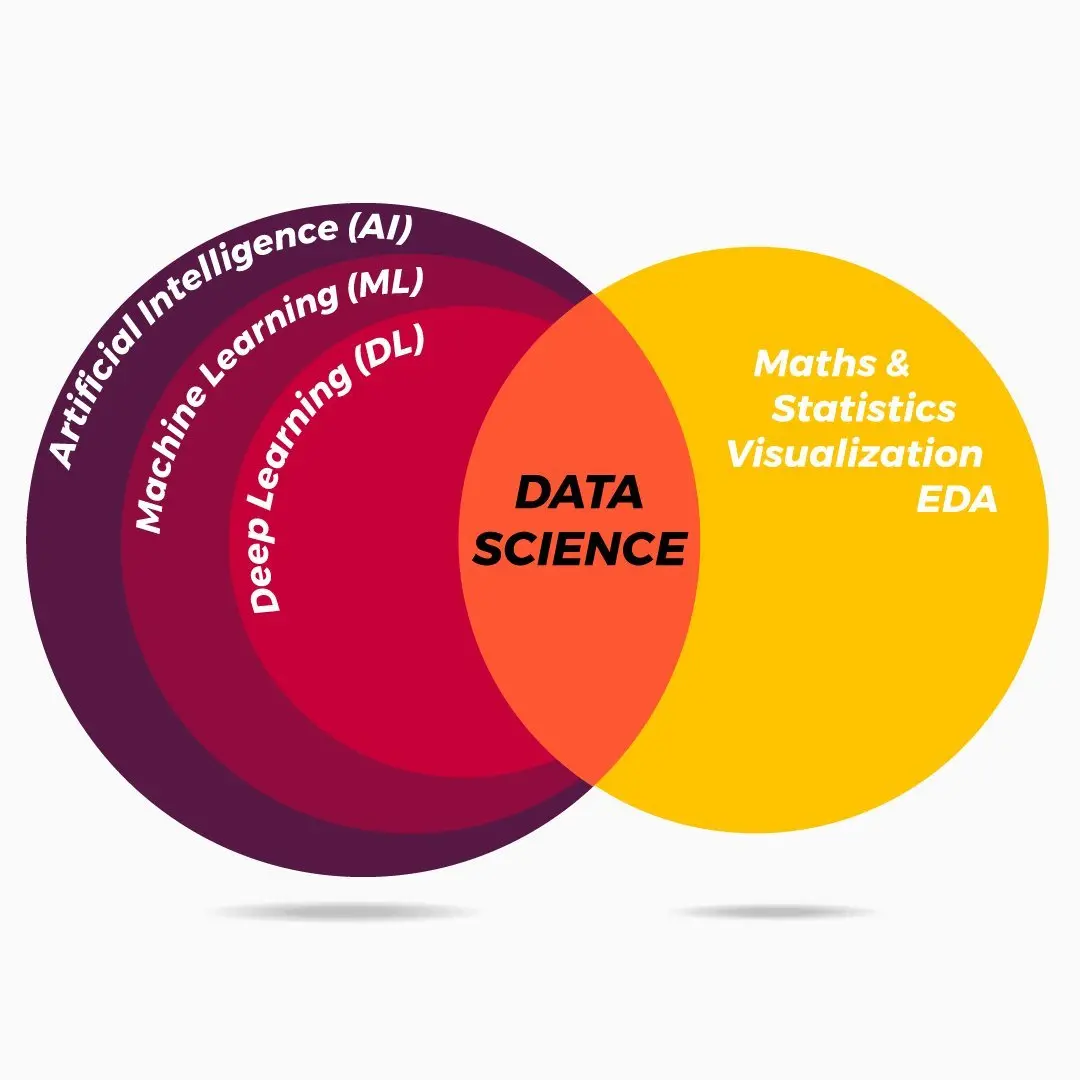
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that involves the use of algorithms and statistical models to enable machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. ML algorithms can be classified into three main types: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broader field that aims to create machines that can perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence, including problem-solving, decision-making, and natural language understanding. AI is composed of multiple subfields, including ML, natural language processing, robotics, computer vision, and more.
Deep Learning (DL) is a subset of ML that uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to learn and extract high-level representations of data. DL has been used to achieve state-of-the-art results in tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
Data Science (DS) is an interdisciplinary field that involves the extraction, analysis, and interpretation of data using statistical and computational methods to extract insights and knowledge from data. DS combines skills and techniques from various fields, including statistics, mathematics, computer science, and domain-specific knowledge, to derive insights and make decisions from data.
In summary, AI is the broadest field that encompasses ML and DL, which are specific subfields of AI. Data Science is a separate field that uses statistical and computational techniques to extract insights and knowledge from data. While they are all related, each field has its own unique focus and set of tools and techniques.
Types of Machine Learning
There are three main types of Machine Learning: Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning, and Reinforcement Learning.
- Supervised Learning: This type of machine learning involves training the model using a labeled dataset, which means the input data is already labeled with the desired output. The model learns to predict the output for new and unseen data based on the patterns and relationships it has learned from the labeled data. Some examples of supervised learning include:
Image Classification: Identifying whether an image contains a cat or a dog
Spam Detection: Classifying emails as spam or non-spam
Sentiment Analysis: Predicting whether a review is positive or negative
- Unsupervised Learning: This type of machine learning involves training the model on an unlabeled dataset, which means the input data is not labeled with the desired output. The model learns to identify patterns and relationships in the data without any guidance, and it groups similar data points together based on their similarities. Some examples of unsupervised learning include:
Clustering: Grouping customers based on their purchase history or behavior
Anomaly Detection: Identifying unusual patterns or outliers in a dataset
Dimensionality Reduction: Reducing the number of features in a dataset while retaining the most important information
- Reinforcement Learning: This type of machine learning involves training the model to make decisions based on trial and error. The model learns by interacting with its environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties based on its actions. The goal of the model is to maximize the rewards it receives by learning from its mistakes. Some examples of reinforcement learning include:
Game Playing: Learning to play chess, go or other games by playing against itself or other opponents
Robotics: Learning to perform tasks such as walking, grasping objects, or navigating a maze
Recommendation Systems: Learning to recommend products or content based on user feedback and preferences.
Examples
There are many real-life applications of Machine Learning (ML) across various industries. Here are some examples:
Image and speech recognition: Image and speech recognition technology uses ML algorithms to enable machines to recognize and understand images and spoken language. Some common applications of this technology include virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, facial recognition technology used in security systems, and self-driving cars.
Fraud detection: Financial institutions and credit card companies use ML algorithms to detect fraudulent transactions in real time. This technology enables companies to quickly identify and stop fraudulent transactions, protecting both the company and the customer.
Healthcare: ML is used in healthcare to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs. It can be used to identify patterns in patient data to enable early detection and treatment of diseases, as well as to develop personalized treatment plans.
Manufacturing: Manufacturing companies use ML algorithms to optimize their production processes, reduce waste, and improve product quality. For example, Tesla uses ML algorithms to improve the efficiency of their battery manufacturing process and to develop their autonomous driving technology.
Customer service: Many companies use ML algorithms to improve their customer service operations. This can include chatbots that can answer customer questions and resolve issues, as well as personalized marketing campaigns that are tailored to each individual customer's preferences and behavior.
This was just a short intro for the ML series that I will start (eventually). There isn't much to learn from this blog, but it can serve as an intro for someone just starting out. If you did find this helpful, stay tuned/like/all that good stuff. Will write on more topics. If you still have any questions/queries you can reach out to me on my LinkedIn / GitHub / Twitter.
Cheers!